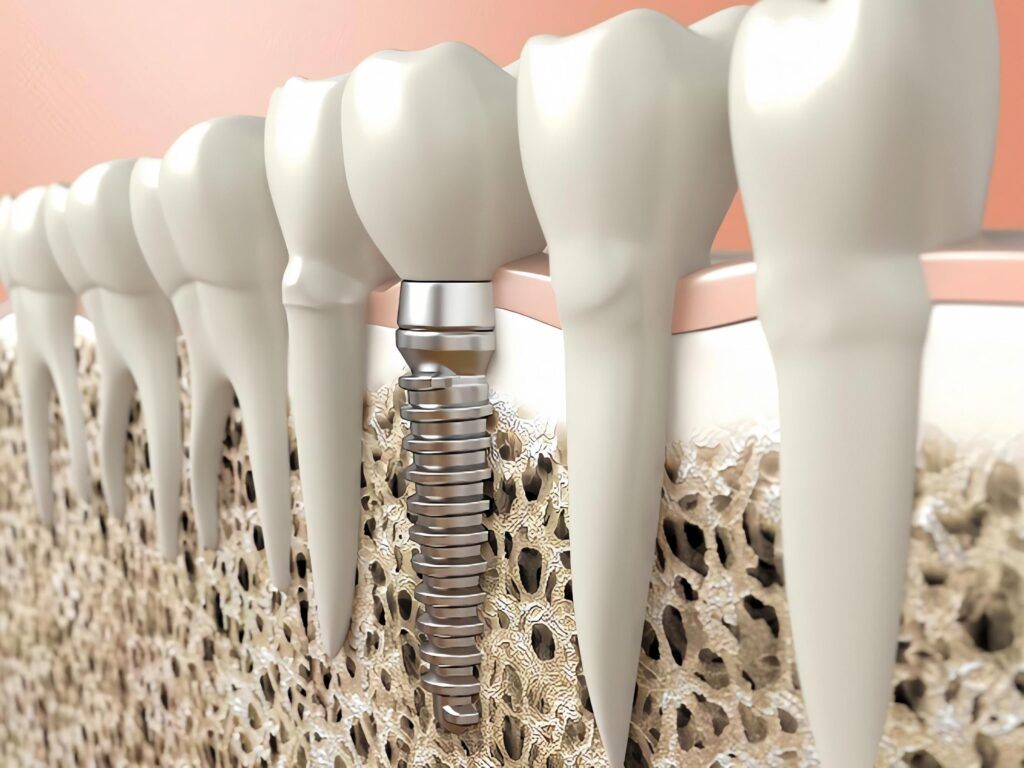
Dental implants have revolutionized the field of restorative dentistry, offering a durable and natural-looking solution for missing teeth. However, for individuals with osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weakened bones, the prospect of getting dental implants can raise several concerns. Osteoporosis affects bone density and strength, which are critical factors for the successful placement and longevity of dental implants. In this blog, we will explore the unique challenges and considerations for individuals with osteoporosis seeking dental implants. By understanding the necessary precautions and treatment options, patients can confidently embark on their dental implant journey, ensuring a healthier and more beautiful smile.
In This Blog:
- Understanding Osteoporosis
- The Impact of Osteoporosis on Dental Implants
- Pre-Implant Assessment and Planning
- Treatment Options and Techniques
- Managing Osteoporosis to Support Dental Implant Success
- The Dental Implant Procedure for Patients with Osteoporosis
Understanding Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a medical condition characterized by a decrease in bone density and an increase in bone fragility, which makes bones more susceptible to fractures. This condition primarily affects older adults, particularly postmenopausal women, but it can also occur in men and younger individuals. Osteoporosis often develops silently over several years, with no symptoms until a fracture occurs. Common risk factors include aging, hormonal changes, family history, insufficient intake of calcium and vitamin D, sedentary lifestyle, and certain medications or medical conditions.
The impact of osteoporosis on bone health is significant, as it leads to the thinning and weakening of bones, making them porous and brittle. This reduced bone quality poses a challenge for dental implants, which rely on the jawbone’s strength and density to provide a stable foundation for the artificial teeth. In individuals with osteoporosis, the jawbone may not be as robust, raising concerns about the ability of the bone to integrate with and support the implants effectively.
Understanding osteoporosis is crucial for those considering dental implants because it allows for a more informed and tailored approach to treatment. With proper management of osteoporosis and collaboration between dental and medical professionals, it is possible to achieve successful dental implant outcomes even in the presence of this bone-weakening condition.
The Impact of Osteoporosis on Dental Implants
Bone health is a critical factor in the success of dental implants. Dental implants require a stable and healthy jawbone to anchor securely and support the artificial teeth. Osteoporosis, which causes bones to become less dense and more fragile, can present several challenges for those seeking dental implants.
Why Bone Health is Crucial for Dental Implants
Dental implants function by integrating with the jawbone through a process called osseointegration. This process ensures that the implant remains stable and can withstand the forces of chewing and biting. Healthy bone tissue is essential for osseointegration, providing the necessary support for the implant. In patients with osteoporosis, the compromised bone density can impede this process, leading to a higher risk of implant failure.
Potential Challenges of Getting Dental Implants with Osteoporosis
- Reduced Bone Density: Osteoporosis can lead to insufficient bone mass in the jaw, making it difficult for the implants to achieve a stable foundation. This can result in poor osseointegration and implant instability.
- Increased Risk of Fractures: Fragile bones are more prone to fractures during the implant placement procedure, complicating the surgical process and potentially prolonging recovery times.
- Healing and Recovery: Osteoporosis can impair the body’s ability to heal efficiently after surgery. This slower healing process can affect the integration of the implant with the jawbone, necessitating longer recovery periods and additional care.
- Medication Interactions: Many individuals with osteoporosis take medications such as bisphosphonates to manage their condition. These medications can impact bone remodeling and healing, influencing the success of dental implants. It is crucial to discuss any medications with both your dentist and physician before undergoing implant surgery.
Importance of Consulting with Both Your Dentist and Physician
For patients with osteoporosis considering dental implants, a multidisciplinary approach is essential. Consulting with both your dentist and physician ensures that all aspects of your health are taken into account. Your physician can provide insights into your overall bone health and any medications you are taking, while your dentist can assess your jawbone’s suitability for implants and plan the procedure accordingly.
By working together, your healthcare providers can develop a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses the unique challenges posed by osteoporosis, ultimately increasing the likelihood of a successful dental implant outcome.
Pre-Implant Assessment and Planning
Proper assessment and planning are crucial steps in ensuring the success of dental implants for patients with osteoporosis. This involves a thorough evaluation by both dental and medical professionals to determine the best approach and to address any potential challenges posed by the condition.
Bone Density Tests and Diagnostic Tools:
Before proceeding with dental implants, a detailed evaluation of bone density is essential. This typically involves imaging tests such as dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scans to measure bone mineral density. Dental imaging, including panoramic X-rays and CT scans, provides a clear view of the jawbone structure and identifies areas that may need special attention.
Medical History Review and Current Medication Assessment:
A thorough review of the patient’s medical history helps in understanding the extent of osteoporosis and any related health issues. It’s vital to assess all medications the patient is currently taking, especially bisphosphonates or other osteoporosis treatments, as they can influence bone healing and implant integration.
Coordination Between Dentist and Physician:
Effective communication and collaboration between the dental surgeon and the patient’s primary care physician or endocrinologist are essential. This ensures that all medical considerations are addressed, and a safe and effective treatment plan is developed. The dentist may need to adjust the treatment plan based on the physician’s recommendations regarding osteoporosis management.
Considering Alternative Implant Techniques or Supplemental Treatments:
In some cases, traditional dental implants may not be suitable for patients with severe osteoporosis. Alternative techniques, such as mini implants or zygomatic implants, might be considered as they require less bone density for placement. Bone grafting or augmentation procedures can be performed to enhance the jawbone structure before implant placement. This involves using bone graft materials to build up the deficient areas, providing a stronger foundation for the implants.
By conducting a comprehensive evaluation and collaborating closely with healthcare providers, dental professionals can develop a personalized treatment plan that accommodates the unique needs of patients with osteoporosis. This tailored approach helps to mitigate risks and enhances the chances of a successful dental implant outcome, allowing patients to enjoy the benefits of a restored smile with confidence.
Treatment Options and Techniques
For patients with osteoporosis, traditional dental implant procedures might require modifications or alternative approaches to ensure successful outcomes. Understanding the various treatment options and techniques available can help tailor the dental implant process to meet the specific needs of individuals with compromised bone health.
Mini Implants:
Mini implants are smaller in diameter compared to standard implants, requiring less bone density for placement. They are often used for securing dentures and can be a viable option for patients with osteoporosis due to their minimally invasive nature and reduced need for extensive bone support.
Zygomatic Implants:
Zygomatic implants are longer and anchored in the cheekbone (zygomatic bone) rather than the jawbone. This technique is beneficial for patients with severe bone loss in the upper jaw, providing an alternative when traditional implants are not feasible.
Bone Grafting and Augmentation Procedures
Bone grafting involves adding bone or bone-like materials to the jawbone to create a solid foundation for implants. This procedure is often necessary for patients with significant bone loss due to osteoporosis. It helps to regenerate bone and improve the stability of the dental implants. There are different types of bone grafting techniques, including:
- Autografts: Using the patient’s own bone, typically harvested from another part of the body.
- Allografts: Using donor bone from a bone bank.
- Xenografts: Using bone from an animal source, usually bovine.
- Synthetic Grafts: Using man-made materials that mimic natural bone.
Use of Advanced Technologies
Advanced imaging and computer software are used to create a precise surgical plan for implant placement. This technology allows for accurate placement of implants in the optimal position, reducing the risk of complications and enhancing the stability of the implants, especially important for patients with osteoporosis.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy:
PRP therapy involves using the patient’s own blood to promote healing and bone regeneration.
The concentrated platelets and growth factors in PRP can enhance the healing process and improve the integration of dental implants with the bone.
By utilizing these specialized treatment options and techniques, dental professionals can overcome the challenges posed by osteoporosis and provide patients with effective and lasting dental implant solutions. Tailoring the approach to the patient’s specific bone health needs ensures a higher success rate and helps patients achieve a functional and aesthetically pleasing smile.
Managing Osteoporosis to Support Dental Implant Success
Effective management of osteoporosis is crucial to ensure the success of dental implants. By maintaining optimal bone health, patients can enhance the stability and longevity of their implants.
Medication Options and Their Implications for Dental Health:
- Bisphosphonates: Commonly prescribed to prevent bone loss, these medications can impact bone remodeling. It’s essential to discuss the timing and duration of bisphosphonate therapy with both your dentist and physician, as it can affect implant integration.
- Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs): These drugs help maintain bone density and may be part of your osteoporosis treatment plan.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): Particularly for postmenopausal women, HRT can help maintain bone density and support overall bone health.
Lifestyle Changes to Improve Bone Health:
- Diet: Ensure adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D through diet and supplements. Foods rich in calcium include dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods. Vitamin D can be obtained from sunlight exposure and dietary sources such as fatty fish and fortified products.
- Exercise: Engage in weight-bearing and resistance exercises to strengthen bones and improve overall bone health. Activities such as walking, jogging, weightlifting, and yoga are beneficial.
- Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can weaken bones and impair healing. Reducing or eliminating these habits can positively impact bone health and the success of dental implants.
Regular Monitoring and Follow-Up Care:
- Schedule regular check-ups with your dentist and physician to monitor bone health and the condition of your dental implants.
- Follow your physician’s recommendations for managing osteoporosis, including regular bone density tests and medication adjustments.
Integrated Care Approach:
- Ensure that your healthcare providers communicate and collaborate to provide a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses both osteoporosis and dental health.
- Discuss any changes in your health or medication regimen with both your dentist and physician to ensure coordinated care.
The Dental Implant Procedure for Patients with Osteoporosis
Understanding the dental implant procedure and the special considerations for patients with osteoporosis can help alleviate concerns and prepare you for a successful outcome.
Initial Consultation and Evaluation:
During the initial visit, your dentist will assess your oral health, review your medical history, and conduct necessary imaging tests to evaluate bone density and structure. A personalized treatment plan will be developed based on your specific needs and bone health status.
Preparation and Pre-Surgery Planning:
Depending on your bone density, your dentist may recommend bone grafting or other preparatory procedures to enhance bone support for the implants. Your dentist will discuss the type of anesthesia to be used and provide instructions for pre-surgery preparation.
Implant Placement Surgery:
The dental implant surgery involves placing the implant into the jawbone. For patients with osteoporosis, special techniques may be used to ensure optimal implant stability. The surgery is typically performed under local anesthesia, sedation, or general anesthesia, depending on the complexity and patient preference.
Healing and Osseointegration:
After the implant is placed, a healing period is necessary for osseointegration, where the implant fuses with the bone. This process may take several months. During this period, your dentist will provide instructions for care and maintenance to promote healing.
Placement of the Abutment and Crown:
Once osseointegration is complete, an abutment is attached to the implant, and a custom-made crown is placed on top. The final restoration provides a natural-looking and functional replacement for the missing tooth.
Special Considerations During Surgery
Anesthesia Options and Comfort Measures:
- Your dentist will discuss anesthesia options to ensure your comfort during the procedure, considering any medical conditions and medications.
- Pain management strategies will be implemented to minimize discomfort during and after the surgery.
Surgical Techniques Tailored for Osteoporotic Patients:
- Specialized techniques, such as the use of shorter or mini implants, may be employed to accommodate lower bone density.
- Advanced technologies, such as computer-guided surgery, can enhance precision and reduce the risk of complications.
By understanding the dental implant procedure and the specific considerations for managing osteoporosis, patients can approach the process with confidence. Proper preparation, effective management of osteoporosis, and collaboration with healthcare providers can significantly enhance the chances of a successful dental implant outcome, leading to improved oral health and quality of life.
Conclusion:
Navigating the journey of getting dental implants with osteoporosis may present unique challenges, but with proper management and a comprehensive treatment plan, achieving a healthy and confident smile is entirely possible. Understanding osteoporosis, working closely with your healthcare providers, and utilizing advanced techniques and technologies can significantly enhance the success of dental implants. By taking proactive steps to maintain bone health and following a tailored approach, patients with osteoporosis can enjoy the benefits of stable, functional, and aesthetically pleasing dental implants. Embrace the opportunity to restore your smile and improve your quality of life with confidence, knowing that the right care and expertise can make all the difference.