Did you know that gum disease is the leading cause of tooth loss in adults? In fact, according to the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research, over 50% of American adults have some form of periodontal disease. If you are one of them, it’s important to understand what periodontal disease is and how it can be treated. In this blog post, we will discuss everything you need to know about periodontal disease!
What is Periodontal Disease?
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a condition in which the gums and supporting structures of the teeth become inflamed. This inflammation can eventually lead to bone loss and tooth loss. There are two main types of periodontal disease: gingivitis and periodontitis.
Gingivitis is the early stage of periodontal disease and is characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums. If gingivitis is left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis. Periodontitis is a more serious form of gum disease that leads to the breakdown of the supporting structures around the teeth. This can eventually lead to tooth loss.
There are also different forms of periodontitis, such as:
- Chronic periodontitis: This is the most common type of periodontitis. It usually progresses slowly and can lead to bone loss.
- Aggressive periodontitis: This form of periodontitis progresses quickly and can often lead to tooth loss in young adults.
- Necrotizing periodontal disease: This is a rare form of periodontitis that can occur in people with HIV/AIDS or other immunocompromised conditions. It is characterized by the death of gum tissue.
What are the Symptoms of Periodontal Disease?
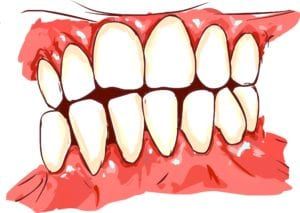
The symptoms of periodontal disease vary depending on the type and severity of the disease. In its early stages, gingivitis may not cause any symptoms. Gingivitis can also cause the gums to bleed easily. As the disease progresses, you may experience:
- Swollen, red, or bleeding gums
- Gums that are tender or painful when touched
- Receding gums
- Bad breath
- Loose teeth
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to see a dentist or periodontist as soon as possible.
What Causes Periodontal Disease?
There are a variety of factors that can contribute to the development of periodontal disease. These include:
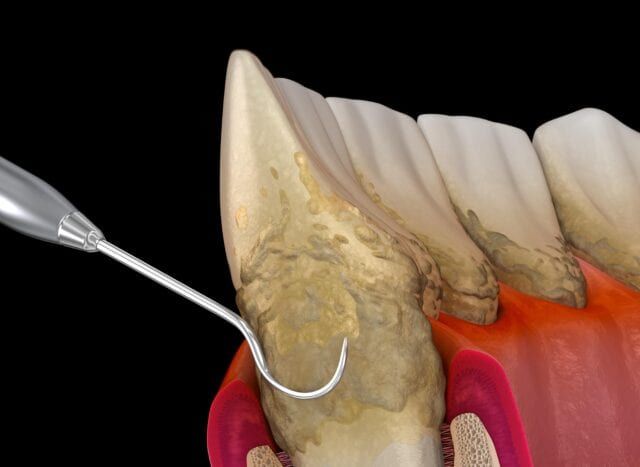
- Plaque: Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. If plaque is not removed with regular brushing and flossing, it can harden and turn into tartar.
- Tartar: Tartar is a hard deposit that can form on the teeth. It is difficult to remove and can only be removed by special tools used by your dentist. If tartar is not removed with regular dental cleanings, then it can accumulate and cause gum inflammation.
- Gum recession: Gum recession is when the gums pull away from the teeth. This can leave the roots of the teeth exposed and create pockets for bacteria to accumulate. Unfortunately, gum recession is both a cause and a result of gum disease.
- Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for the development of periodontal disease. This is because smoking impairs proper blood circulation and impairs the gum’s ability to heal themselves.
- Diabetes: Diabetes can increase the risk of developing periodontal disease. One of the ways diabetes increases the risk of periodontal disease is by damaging the blood vessels. This can impair blood circulation and make it difficult for the gum tissue to heal properly. Additionally, people with diabetes are more likely to develop infections, which can also lead to periodontal disease.
- Dry Mouth: Dry mouth is when there is not enough saliva in the mouth. This can be caused by certain medications or medical conditions. Dry mouth increases the risk of developing periodontal disease because it allows plaque to build up on the teeth more easily.
How to Prevent and/or Treat Periodontal Disease?
The best way to prevent periodontal disease is to practice good oral hygiene. This means brushing your teeth twice a day and flossing once a day. It’s also important to see a dentist for regular checkups and cleanings.
Your dentist or periodontist can diagnose periodontal disease by examining your teeth and gums. They may also take X-rays of your teeth to look for signs of bone loss. If you are experiencing symptoms of gum disease, they will also ask about your medical history and whether you smoke.
If you already have periodontal disease, there are a few different treatment options available. Treatment for periodontal disease depends on the severity of the disease. In its early stages, gingivitis can be treated with a professional cleaning and improved oral hygiene. More advanced cases of periodontitis may require more aggressive treatment, such as:
- Scaling and root planing: This is a deep cleaning procedure that involves removing plaque and tartar from the teeth and roots. It is usually performed by a dentist or periodontist.
- Antibiotics: These are usually applied through the use of special trays that fit over the teeth and gums. A medicated mouthwash may also be used.
- Surgery: In severe cases of periodontitis, surgery may be necessary to clean the teeth and roots. Surgery may also be necessary to repair damaged bone or gum tissue.
How Periodontal Disease Affects Dental Implants
Some people assume that dental implants are resistant to dental issues. Although dental implants cannot decay like natural teeth, they are still susceptible to the effects of gum disease. This is because periodontal disease can damage the bones and tissues that support the implants. If you get dental implants while you have periodontal disease, there is a greater risk that the implants will fail.
There are two forms of periodontal disease that can affect someone with dental implants:
- Peri-mucositis: This is an infection of the mucous membrane that surrounds the implant.
- Peri-implantitis: This is a more serious form of peri mucositis that involves inflammation and bone loss around the implant.
If you have dental implants, it’s important to practice good oral hygiene and see a dentist or periodontist for regular checkups and cleanings. If you develop periodontal disease, it’s important to get treatment as soon as possible to prevent damage to the implants. This is because implant failure can occur when the bone and tissue around the implant begin to deteriorate due to peri-implantitis or peri-mucositis.
In Conclusion
Periodontal disease is a serious condition that can lead to tooth loss. If you think you might have periodontal disease, it’s important to see a dentist so that the proper treatment can be administered. With proper treatment, periodontal disease can be controlled and the damage it causes can be managed to prevent future complications, such as implant failure.
We hope this blog post has helped you to better understand periodontal disease. If you have any questions, please feel free to contact us. We would be more than happy to help!